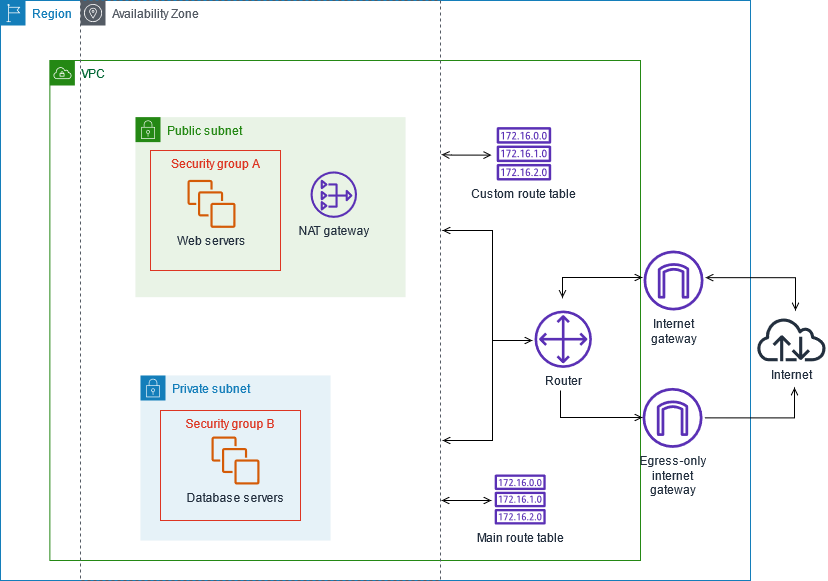
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud computing platform that offers a range of services for businesses and individuals to run their applications and store their data. AWS offers both public and private services, and understanding the differences between the two can help businesses determine which services are best suited for their needs.
Public Services
Public services in AWS are those that are available to anyone with an AWS account. These services are accessible via the internet and are designed for use by individuals, startups, and small to medium-sized businesses. Some examples of public services in AWS include Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3), and Amazon Relational Database Service (RDS).
Public services are offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, which means that customers only pay for the resources they use. This model is particularly beneficial for businesses that have variable workloads or that need to scale up or down quickly. Public services in AWS are also highly scalable, meaning that customers can quickly add or remove resources to meet their changing needs.
Private Services
Private services in AWS are those that are designed for use by larger enterprises and organizations. These services are not accessible via the internet and are instead accessed via a virtual private network (VPN) or a direct connection. Private services are typically used by businesses that need to store sensitive data or that require high levels of security and compliance.
Examples of private services in AWS include Amazon Virtual Private Cloud (VPC), Amazon Elastic File System (EFS), and Amazon WorkSpaces. Private services are typically more expensive than public services, as they require more resources to set up and maintain. However, they offer a higher level of security and control, as well as greater flexibility and customization.
Differences between Public and Private Services
The main differences between public and private services in AWS are accessibility, security, and cost. Public services are accessible via the internet and are designed for use by individuals and small to medium-sized businesses. They are highly scalable, and customers only pay for the resources they use. Private services, on the other hand, are accessed via a VPN or a direct connection and are designed for use by larger enterprises and organizations. They offer a higher level of security and control, as well as greater flexibility and customization. However, they are more expensive to set up and maintain.
Another key difference between public and private services in AWS is the level of customization and control that customers have over their resources. Public services are designed to be easy to use and require little technical expertise. Private services, on the other hand, are highly customizable and require a greater level of technical expertise to set up and maintain.
Conclusion
AWS offers a range of services to meet the needs of businesses and individuals, from public services that are accessible via the internet to private services that offer a higher level of security and control. Understanding the differences between these services is essential for businesses to determine which services are best suited for their needs. Whether a business chooses public or private services in AWS, they can benefit from the scalability, flexibility, and reliability that AWS offers.